The monthly inflation rate decreased in April.
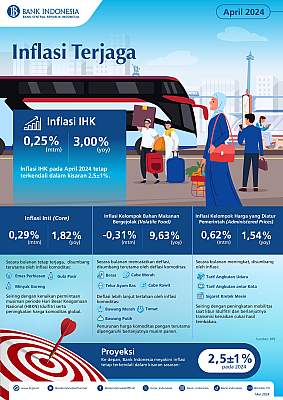
Inflation or the increase in the Consumer Price Index (CPI) in April 2024 was recorded at 0.25%, a monthly decrease compared to the inflation in March which was recorded at 0.52%. Thus, on an annual basis or throughout January-April 2024, inflation reached 3% or slightly decreased compared to January-March which was recorded at 3.10%, but still relatively high compared to the end of 2023 inflation which was only 2.61%.
According to a written statement from Bank Indonesia (BI) through the Director of the Communication Department, Fadjar Majardi, today, the April inflation reported by the Central Statistics Agency (BPS) was maintained within the target range of 2.5±1% for this year. BI claimed that the maintained inflation is the result of consistent monetary policy and the close synergy in inflation control between BI and the government through the Central and Regional Inflation Control Team (TPIP and TPID) by strengthening the National Movement for Food Inflation Control (GNPIP). "In the future, Bank Indonesia believes that inflation will remain under control within the target range," said Fadjar.
Similarly, core inflation remained stable. In April 2024, it recorded a monthly increase of 0.29%, slightly higher than March which was 0.23%, due to the seasonal increase in demand during fasting month and Eid, as well as the increase in global commodity prices, especially gold.
Fadjar stated that core inflation is mainly contributed by the inflation of cooking oil and sugar, in addition to the inflation of gold jewelry commodities. On an annual basis, core inflation in April 2024 recorded 1.82%, an increase compared to the inflation in March which was 1.77%. Core inflation is a component of inflation that tends to be stable or persistent in its movement and is influenced by fundamental factors.
That is, the interaction of supply and demand, external factors such as exchange rates, international commodity prices, and global economic developments, as well as future inflation expectations. Volatile food and energy commodities are not included in the calculation of core inflation. Therefore, core inflation calculations are more related to monetary policy.
Meanwhile, the volatile food group recorded a monthly deflation (decrease in CPI) of 0.31%, compared to March which experienced inflation of 2.16%. The deflation in the volatile food group is mainly contributed by commodities such as red chili, rice, chicken eggs, and bird's eye chili. The prices of various food commodities have declined mainly due to the ongoing harvest season, especially for various types of chili and rice. Deflation is further restrained by inflation in commodities such as shallots, tomatoes, and garlic.
Meanwhile, on an annual basis, the volatile food group experienced inflation of 9.63% (yoy), a decrease compared to March which was 10.33%. "In the future, volatile food inflation is predicted to decrease again, as the harvest season continues, and supported by the synergy of inflation control through various regional programs," wrote the official statement from the central bank.
Inflation in the administered prices group (government-regulated prices) increased drastically in April, with a monthly increase of 0.62%, compared to March which recorded 0.08%. This is mainly influenced by inflation in air transportation tariffs, intercity transportation, and machine-made kretek cigarettes (SKM), in line with increased mobility during the Eid holiday and the continued transmission of tobacco tax increases. On an annual basis (yoy), inflation in the administered prices group recorded 1.54%, an increase compared to March which was only 1.39%.






